This feature is the most reliable way to measure people's emotional attitudes towards a product or service.
Learn more: Semantic differential scale
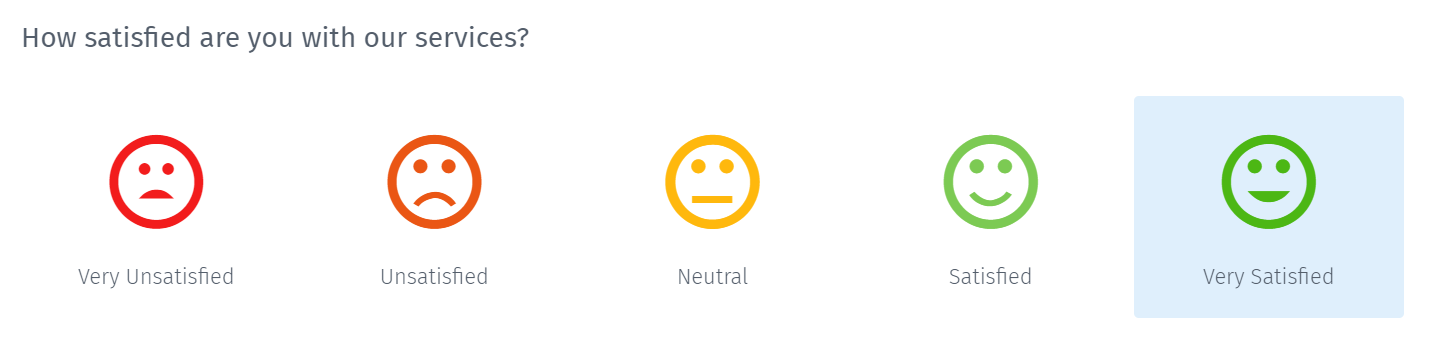
Example of a semantic differential question in a survey
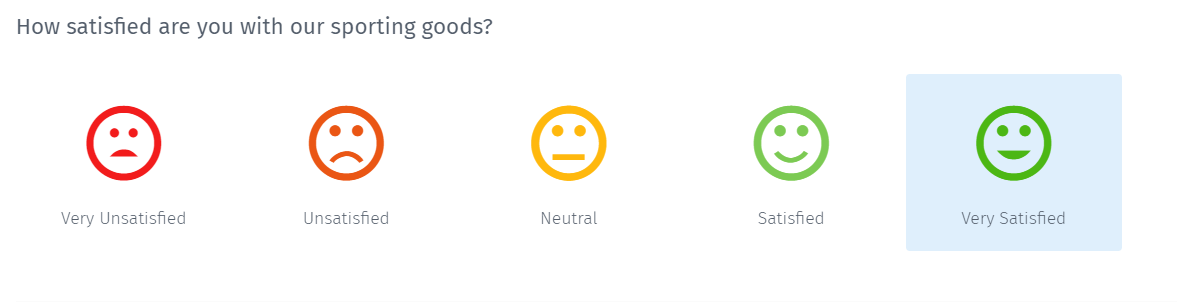
Researchers widely use semantic differential questions in surveys for research. Let's consider a retailer who sells sports goods and wants to know the customers' feedback on how satisfied they are with their quality. To obtain maximum responses, a retailer uses the smiley rating scale, which ranges from very unsatisfied to very satisfied. It helps the retailers know the people's attitudes towards the product and help them stay ahead of the curve from a product and a customer satisfaction standpoint.
The HR department in the organization uses the semantic differential in survey questions to measure employee satisfaction levels.

Uses of semantic differential survey questions
Listed below are the areas where you can use semantic differential questions to derive actionable insights.
Customer attitude: Researchers use semantic differential surveys to measure the customer's attitude towards a specific subject, product, or services. It allows the organization to understand the value of their customers and also enables meeting customer expectations.
Employee satisfaction: Organizations use semantic differential to capture employees' job satisfaction level on a scale of very unsatisfied to very satisfied.
Product/service recommendation: Customer references always help the organization to identify new business opportunities. Considering this, companies must use semantic differential surveys to know whether they will recommend my service or not.
Types of semantic differential questions
Different types of semantic questions are used in surveys depending on the need and response collection method. The most common types are:
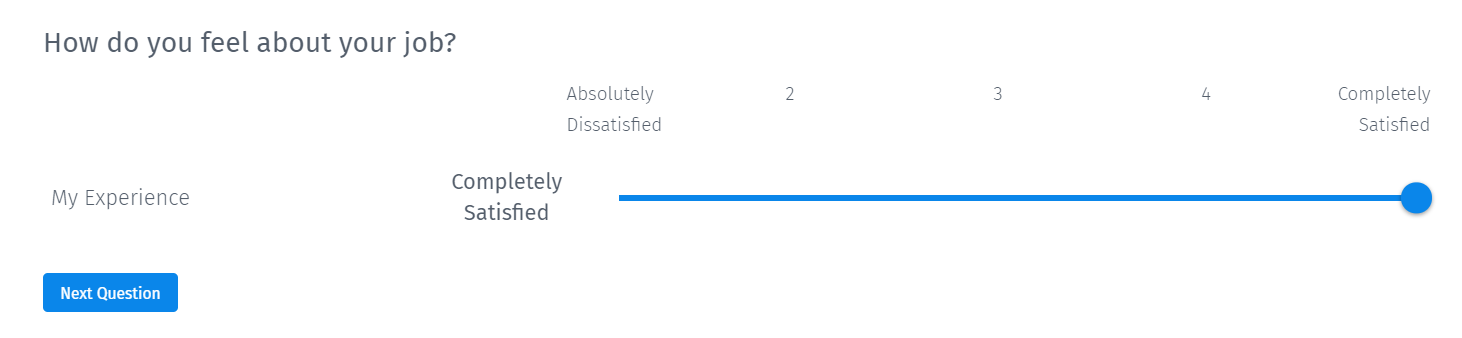
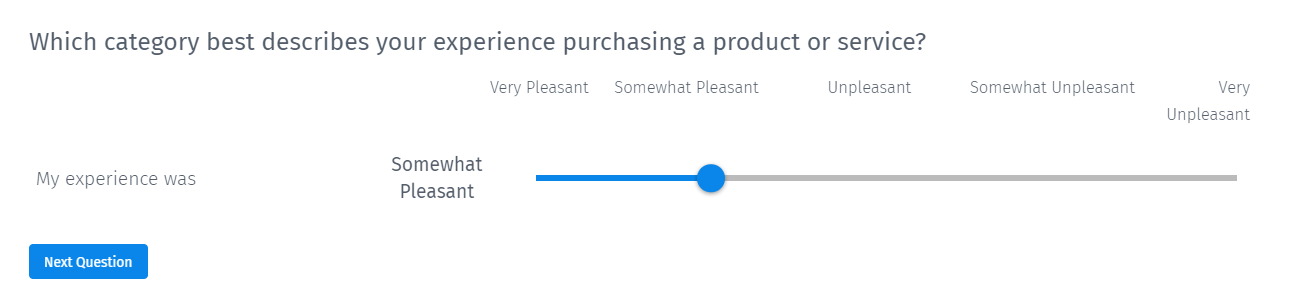
Slider scale question
The slider rating scale question includes the text slider with textual answer options. Based on this, the respondents will leave the indicator at the point where the answer is to be selected.

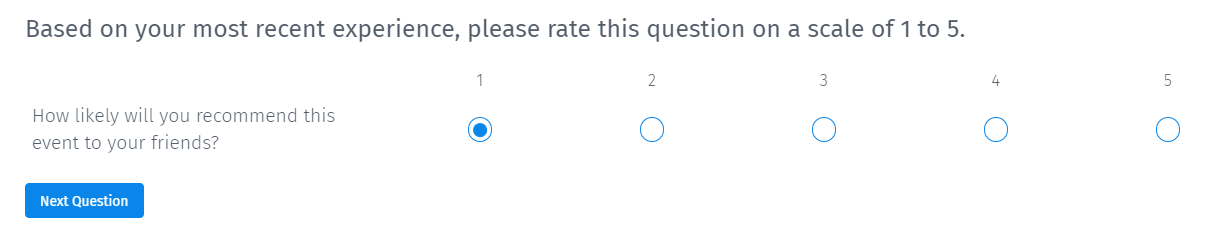
Non-slider scale question
The non-slider rating scale question includes radio buttons, a more traditional survey look, and feels with a scale of
1 to 5.

Smiley-rating scale
The question type with a 5 point rating scale, represents the sentiments from negative to positive. It communicates the emotions that are easy and engaging for the respondents. Adding this question intends to keep engaging the respondents and get a better completion rate.
Learn more: Smiley face question.

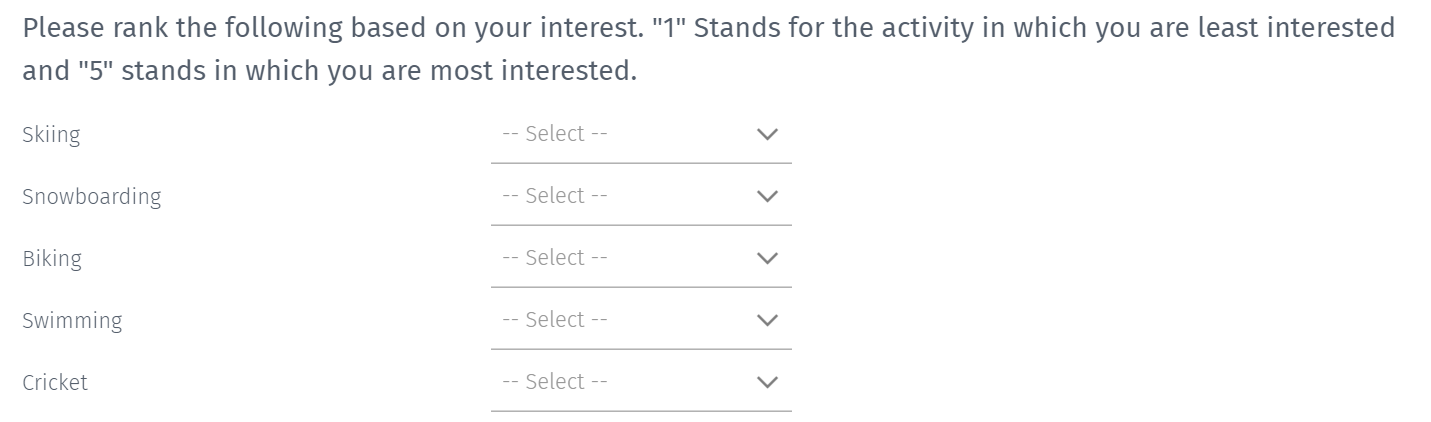
Rank order question
The rank order question allows the respondents to order the product or brands as per their interest. In the below example, a person who loves to swim will rank the answer option as 5, and the person who hates skiing will rate the answer option as "1".
Learn more: Rank order question.

Advantages of using a semantic differential survey
The semantic differential survey is one of the most reliable ways to capture feedback on people's emotions towards a particular entity. Listed below are the three significant advantages of semantic differential:
Reduced survey churn rate: Organizations using semantic differential questions in surveys are more likely to receive maximum responses, and reduced survey dropout rate as the scale is easy to understand.
Accurate data collection: Due to the answer options being diametrically opposite, respondents can easily select the response that they are most comfortable with and best denotes their emotions.
Easy to use and set up: The design of this scale is simple and easy compared to other scales, which results in better engagement and survey completion rates.
How to use a semantic differential question in your surveys?
Explore our help file on semantic differential scale to learn how to use this survey feature.
Survey Software Easy to use and accessible for everyone. Design, send and analyze online surveys.
Research Suite A suite of enterprise-grade research tools for market research professionals.
Customer Experience Experiences change the world. Deliver the best with our CX management software.
Employee Experience Create the best employee experience and act on real-time data from end to end.